By Rinki Pandey September 9, 2025
ECommerce Payments 101 Welcome to the digital marketplace, a world where transactions happen at the speed of a click. For any online business, from a fledgling startup to a global enterprise, the checkout process is the final, most critical step in the customer journey. It’s the moment where a browsing visitor becomes a paying customer. Yet, it’s also where many businesses falter. A clunky, unsecure, or confusing payment system can lead to abandoned carts and lost revenue. This is where a deep understanding of eCommerce Payments 101 becomes not just an advantage, but a necessity.
Mastering the fundamentals of online transactions is the key to unlocking sustainable growth. This comprehensive guide is designed to be your definitive resource for everything related to eCommerce Payments 101. We will demystify the complex world of online payment processing, explore the various gateway options available, delve into the non-negotiable aspects of security, and outline the checkout best practices that convert visitors into loyal customers.
Navigating the landscape of online payments can seem daunting. There are technical terms, security protocols, and a dizzying array of service providers to choose from. However, by breaking it down, you’ll see that a powerful and efficient payment system is well within your reach. This article is your roadmap. Consider this your masterclass in eCommerce Payments 101, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions that will protect your business, build customer trust, and ultimately, drive your success in the competitive world of online retail.
The Core Components of an eCommerce Payment System
Before we can optimize your checkout, it’s essential to understand the machinery working behind the scenes. A successful transaction isn’t just a single event; it’s a rapid-fire communication between several key players. Grasping these core components is the first step in mastering eCommerce Payments 101.
The Merchant Account: Your Business’s Digital Bank Account
Think of a merchant account as a specialized bank account designed specifically to accept and hold funds from credit and debit card transactions. When a customer makes a purchase on your site, the money doesn’t go directly into your standard business bank account. Instead, it’s first routed to your merchant account.
This account acts as an intermediary, holding the funds while they are being cleared and verified. Once the transaction is approved and processed, the funds are then transferred (or “settled”) into your regular business account. Obtaining a merchant account requires an application process where a financial institution assesses your business’s risk profile. Understanding its role is a foundational piece of the eCommerce Payments 101 puzzle.
The Payment Gateway: The Secure Bridge Between Your Store and the Banks
The payment gateway is the secure digital messenger of your online store. It’s the technology that connects your website’s shopping cart to the payment processing network. When a customer enters their credit card details and clicks “Buy Now,” the payment gateway takes over.
Its primary job is to securely capture that sensitive payment information, encrypt it, and send it to the payment processor for authorization. It’s the virtual equivalent of the physical point-of-sale (POS) terminal you see in a brick-and-mortar store. A reliable payment gateway is absolutely central to the practice of secure eCommerce Payments 101.
The Payment Processor: The Transaction Workhorse
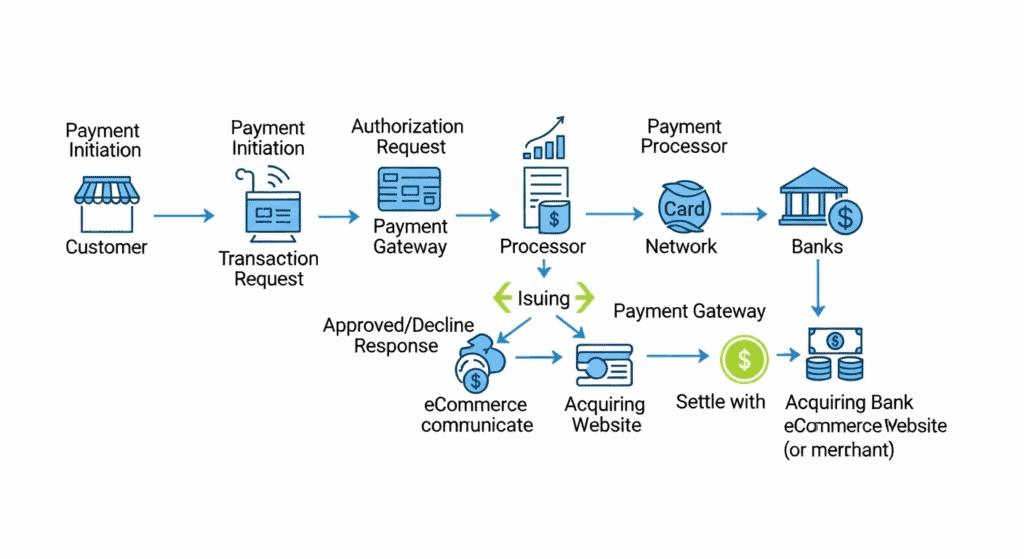
The payment processor is the entity that facilitates the actual transaction. It communicates the transaction details between your merchant account, the customer’s bank (the issuing bank), and your bank (the acquiring bank).
The processor sends the authorization request through the card networks (like Visa, Mastercard, or American Express) to the customer’s bank. The customer’s bank then checks for sufficient funds and fraud indicators before sending back an approval or decline message. This entire complex communication happens in a matter of seconds. The processor handles the heavy lifting, making it a vital component in the eCommerce Payments 101 ecosystem.
How These Components Work Together (A Step-by-Step Flow)
To truly understand eCommerce Payments 101, let’s walk through a typical transaction:
- Purchase Initiation: A customer selects products on your website and proceeds to the checkout page.
- Information Entry: The customer enters their payment details (credit card number, expiry date, CVV) into your checkout form.
- Gateway Takes Over: Your website securely transmits this encrypted information to the payment gateway. The gateway ensures the data is protected during its journey.
- Processor Communication: The payment gateway forwards the transaction details to the payment processor.
- Authorization Request: The processor routes the request to the appropriate card network (e.g., Visa), which then sends it to the customer’s issuing bank.
- Bank Approval/Denial: The issuing bank checks the customer’s account for funds and assesses the transaction for risk. It sends an approval or decline code back through the same chain.
- Response Relay: This response travels from the processor back to the gateway, which then communicates the result (e.g., “Transaction Approved” or “Transaction Failed”) to your website.
- Order Fulfillment: If approved, your website displays a confirmation message, and you can begin fulfilling the order.
- Settlement: The approved funds are held in your merchant account and are later transferred to your primary business bank account in a batch, a process known as settlement.
Unpacking Payment Gateway Options: Choosing the Right Fit
Not all payment gateways are created equal. The type you choose will significantly impact your customer’s checkout experience, your development requirements, and your security responsibilities. This is a critical decision point in your eCommerce Payments 101 journey. Broadly, they fall into three categories.
Hosted Payment Gateways (Off-site Payments)
Hosted gateways, also known as redirect gateways, take the customer away from your website to complete the payment on the provider’s secure page. PayPal Standard is a classic example.
- Pros: The biggest advantage is security. The gateway provider handles all the sensitive data and PCI compliance, significantly reducing your security burden. They are also typically very easy and fast to set up.
- Cons: The main drawback is the user experience. Redirecting customers to another site can be jarring and may lead to a drop in conversions, as some customers may not trust the new page or simply abandon the process. This is a key consideration for eCommerce Payments 101.
Self-Hosted Payment Gateways (Direct Payments)
With a self-hosted or direct gateway, the customer enters their payment information directly on your checkout page. The data is collected on your site and then sent to the gateway’s backend for processing. Stripe and Braintree are popular examples that operate this way.
- Pros: This offers a much more seamless and professional checkout experience, as the customer never leaves your site. This control over the user interface can significantly boost conversion rates.
- Cons: The responsibility for security is much higher. You are handling sensitive cardholder data, which means you must ensure your site is secure and fully PCI DSS compliant. This is a more complex aspect of eCommerce Payments 101.
API-Hosted Payment Gateways (Integrated Payments)
API (Application Programming Interface) hosted gateways offer the highest level of customization and control. You use the provider’s API to build a completely custom checkout experience directly within your site and mobile app. All payment details are collected and processed via the API.
- Pros: Unmatched control over the look, feel, and functionality of your checkout process. Ideal for larger businesses with specific needs and the development resources to build a bespoke solution.
- Cons: This is the most complex option to implement and maintain. It places the full weight of PCI DSS compliance and data security squarely on your shoulders. It requires significant technical expertise, a core challenge in advanced eCommerce Payments 101.
Comparison Table: Hosted vs. Self-Hosted vs. API-Hosted
To make this crucial eCommerce Payments 101 decision easier, here is a detailed breakdown of the key differences:
| Feature | Hosted Gateway (Redirect) | Self-Hosted Gateway (Direct) | API-Hosted Gateway (Integrated) |
| Customer Experience | Can be disjointed; customer leaves your site to pay. | Seamless; customer stays on your site throughout the process. | Fully customized and seamless; integrated into your site/app. |
| Security Burden | Low; the gateway provider handles PCI compliance and data security. | Medium; you are responsible for securing your site (e.g., SSL), but the provider helps with PCI validation. | High; you are fully responsible for PCI DSS compliance and securing all cardholder data. |
| Customization | Very limited; you have little to no control over the payment page’s appearance. | Moderate; you control the checkout form on your site, but the underlying process is managed by the provider. | Complete; you have full control over the entire user interface and experience. |
| Implementation | Easy and fast; often just requires setting up an account and adding a button. | Moderately complex; requires some development work to integrate with your website. | Highly complex; requires significant development resources and technical expertise. |
| Best For | Small businesses, startups, or those prioritizing simplicity and low security overhead. | Most small to medium-sized businesses looking for a balance of good user experience and manageable security. | Large enterprises, platforms, and businesses with unique needs and dedicated development teams. |
Choosing the right gateway is a foundational decision in your eCommerce Payments 101 strategy. It requires a careful evaluation of your business’s priorities, technical capabilities, and risk tolerance.
The Crucial Role of Security in eCommerce Payments 101
In the world of online transactions, trust is your most valuable currency. A single security breach can not only lead to devastating financial losses but can also permanently damage your brand’s reputation. Therefore, robust security isn’t an option; it’s the absolute bedrock of any successful eCommerce Payments 101 strategy.
Understanding PCI DSS Compliance
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security standards designed to ensure that all companies that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment.
Achieving and maintaining PCI compliance is mandatory for any business that handles card payments. The requirements are extensive, covering everything from network security and data encryption to physical access controls. The type of payment gateway you choose heavily influences your PCI compliance scope. A hosted gateway minimizes your responsibility, while an API-hosted gateway maximizes it. A deep dive into PCI DSS is a non-negotiable part of any eCommerce Payments 101 education.
The Power of SSL/TLS Encryption
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), and its modern successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS), are cryptographic protocols that provide secure communication over a computer network. An SSL/TLS certificate on your website encrypts the data exchanged between a customer’s browser and your server.
You can identify a secure site by the “https://” in the URL and the padlock icon in the address bar. This is a fundamental security measure that protects sensitive information, like login credentials and payment details, from being intercepted by malicious actors. No modern eCommerce store should operate without it; it’s a basic requirement of eCommerce Payments 101.
Tokenization: Securing Data by Replacing It
Tokenization is a powerful security process that replaces sensitive cardholder data with a unique, non-sensitive equivalent known as a “token.” This token has no extrinsic or exploitable value.
When a transaction occurs, the actual card details are sent to the payment gateway, which stores them securely and returns a token to your system. You can then use this token for future transactions (like recurring subscriptions or one-click checkouts) without ever having to store the actual credit card number. This dramatically reduces your security risk and PCI compliance scope, making it a best practice in eCommerce Payments 101.
Advanced Fraud Detection and Prevention Tools
Beyond the basics, a comprehensive eCommerce Payments 101 security plan involves proactive fraud prevention. Modern payment systems offer a suite of tools to help you identify and block fraudulent transactions.
- Address Verification System (AVS): This tool checks the billing address submitted by the customer against the address on file with the card-issuing bank.
- Card Verification Value (CVV): This requires the customer to enter the three- or four-digit security code on their card, proving they have physical possession of it.
- 3D Secure (e.g., Verified by Visa, Mastercard SecureCode): This adds an extra layer of authentication, often requiring the customer to enter a password or a one-time code sent to their phone to approve the transaction.
- Velocity Checks and IP Geolocation: These tools can flag suspicious activity, such as multiple transactions from the same IP address in a short period or orders from high-risk countries.
Implementing these tools is a critical part of a multi-layered defense strategy, a key theme in advanced eCommerce Payments 101.
Navigating the Landscape of Payment Methods
Today’s consumers expect choice and flexibility. Limiting your payment options can be just as detrimental as having a slow website. A core principle of eCommerce Payments 101 is to cater to your customers’ preferences by offering a diverse range of payment methods.
Credit and Debit Cards: The Undisputed Kings
Despite the rise of new technologies, credit and debit cards remain the most popular payment method for online purchases globally. Accepting all major card networks—Visa, Mastercard, American Express, and Discover—is absolutely essential. This is the baseline expectation for any online store and the starting point for your eCommerce Payments 101 strategy.
Digital Wallets: The Rise of Convenience
Digital wallets (or eWallets) like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal allow users to store their payment information securely and make purchases with a single click or tap. They offer a fast, frictionless checkout experience, especially on mobile devices.
The convenience factor is a massive driver of conversion. Integrating these popular digital wallets can significantly reduce cart abandonment and is a smart move for any business looking to modernize its eCommerce Payments 101 approach.
Bank Transfers and ACH Payments
Direct bank transfers, including Automated Clearing House (ACH) payments in the US, allow customers to pay directly from their bank accounts. While less common for typical consumer goods, they are a popular option for B2B transactions, high-value purchases, and subscription-based services due to their lower transaction fees compared to credit cards.
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL): The Modern Layaway
Buy Now, Pay Later services like Klarna, Afterpay, and Affirm have exploded in popularity. They allow customers to purchase a product immediately and pay for it in a series of interest-free installments. Offering BNPL can increase conversion rates and average order value, particularly for younger demographics and for higher-priced items. Including BNPL is becoming a standard best practice in contemporary eCommerce Payments 101.
Cryptocurrencies: A Niche but Growing Option
While still a niche market, accepting cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum can be a differentiator for certain businesses, especially those targeting a tech-savvy audience or operating in the digital goods space. It’s a forward-thinking component of an eCommerce Payments 101 strategy, though it comes with considerations around volatility and regulation.

Mastering Checkout Best Practices for Maximum Conversions
Your payment infrastructure can be perfect, but if your checkout process is poorly designed, you will lose customers. The checkout is where the final decision is made. Optimizing this experience is perhaps the most impactful part of applying your eCommerce Payments 101 knowledge.
Simplicity is Key: Minimizing Form Fields
Every additional field you ask a customer to fill out is another opportunity for them to abandon the purchase. A lengthy and complicated form creates friction. Only ask for the information that is absolutely essential to process the order. Use tools like address auto-fill to make the process even faster. This is a golden rule in eCommerce Payments 101.
Offer Guest Checkout: Don’t Force Registration
Forcing a new customer to create an account before they can make a purchase is one of the biggest conversion killers. It adds a significant barrier to a quick and easy purchase. Always provide a prominent “Guest Checkout” option. You can offer the opportunity to create an account after the purchase is complete, using the information they’ve already provided.
Mobile-First Design: Optimizing for the Small Screen
A significant portion of online shopping now happens on mobile devices. Your checkout process must be fully responsive and easy to navigate on a small screen. This means large form fields, clear buttons, and a design that doesn’t require excessive pinching and zooming. A poor mobile experience is a guaranteed way to lose sales, a critical lesson in eCommerce Payments 101.
Transparent Pricing: Eliminating Surprise Fees
Unexpected costs are the number one reason for cart abandonment. Be upfront about all costs, including shipping, taxes, and any other fees, as early in the process as possible. A price summary that updates in real-time as the customer proceeds through checkout builds trust and prevents last-minute sticker shock.
Clear Calls-to-Action (CTAs)
The buttons that guide the user through the checkout process—like “Proceed to Checkout,” “Continue to Payment,” and “Place Order”—should be clear, concise, and visually prominent. Use action-oriented language and contrasting colors to make it obvious what the next step is. Ambiguity at this stage is a recipe for disaster. This simple principle of user interface design is vital to eCommerce Payments 101.
Displaying Trust Seals and Security Badges
Visibly displaying security badges (like SSL certificates) and trust seals (from services like the Better Business Bureau or Norton) can significantly increase customer confidence. These visual cues reassure customers that their personal and financial information is safe, which is particularly important for first-time buyers who are unfamiliar with your brand. It’s a simple yet powerful element of a complete eCommerce Payments 101 strategy.
The Future of eCommerce Payments: What’s Next?
The world of eCommerce payments is constantly evolving. Staying ahead of the curve is crucial for long-term success. The future of eCommerce Payments 101 will be defined by even greater speed, security, and personalization.
The Growth of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication—using fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice patterns to approve a purchase—is set to become more mainstream. It offers a combination of superior security and ultimate convenience, eliminating the need for passwords or codes. This technology, already common in mobile wallets, will become more deeply integrated into the web checkout experience.
AI and Machine Learning in Fraud Detection
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing fraud detection. These systems can analyze thousands of data points in real-time to identify complex fraud patterns that would be invisible to human analysts. This allows for more accurate fraud prevention with fewer false positives, leading to a smoother experience for legitimate customers. This advanced tech is the new frontier of eCommerce Payments 101.
The Expansion of Invisible Payments
The concept of “invisible payments,” pioneered by services like Uber, will continue to expand. This involves a customer pre-authorizing a payment method, allowing for transactions to happen automatically in the background without any active checkout process. This could manifest in smart appliances that reorder supplies or subscription services that feel completely seamless. As we look ahead, the core concepts of eCommerce Payments 101 will adapt to these increasingly frictionless models.
Your Comprehensive eCommerce Payments 101 Checklist
In conclusion, a well-executed payment strategy is a powerful engine for growth. It’s about much more than simply accepting money; it’s about building trust, reducing friction, and creating a positive customer experience that encourages repeat business.
By understanding the core components of the payment ecosystem, choosing the right gateway for your needs, prioritizing ironclad security, offering a variety of payment methods, and optimizing your checkout flow, you are putting the essential principles of eCommerce Payments 101 into practice.
Remember that this is not a one-time setup. The landscape will continue to change, and customer expectations will evolve. Regularly review your processes, stay informed about new technologies, and always prioritize the security and convenience of your customers. By doing so, you will not only master eCommerce Payments 101 but also build a resilient and thriving online business.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a payment gateway and why do I need one?
A payment gateway is a secure technology service that acts as a middleman between your eCommerce website and the payment processor. You need one to securely capture, encrypt, and transmit your customer’s sensitive credit card information to the processing network for authorization. It’s the essential link that enables you to accept online card payments safely.
2. What is the difference between a payment gateway and a payment processor?
While they work together, they have distinct roles, a common point of confusion in eCommerce Payments 101. The payment gateway is the customer-facing technology that connects to your website and securely captures payment details. The payment processor is the behind-the-scenes entity that facilitates the communication between your bank, the customer’s bank, and the card networks to actually move the money.
3. Why is PCI DSS compliance so important for my online store?
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is a mandatory set of security rules for any business that handles credit card information. Compliance is crucial because it helps protect your business and your customers from data breaches and fraud. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, including hefty fines, and can lead to a complete loss of customer trust and the ability to accept card payments.
4. How can I reduce shopping cart abandonment during the checkout process?
The best strategies, rooted in the principles of eCommerce Payments 101, include offering a guest checkout option, minimizing the number of form fields, being transparent about all costs (like shipping and taxes) upfront, ensuring your checkout is mobile-friendly, and displaying trust seals and security badges to build confidence. Offering multiple payment methods, including digital wallets, also significantly helps.
5. Should I offer multiple payment methods on my website?
Absolutely. Offering a variety of payment methods is a key best practice. Customers have strong preferences, and not providing their preferred option (be it a specific credit card, PayPal, Apple Pay, or a BNPL service) can directly lead to a lost sale. The goal is to make the payment process as convenient as possible for the widest range of customers.